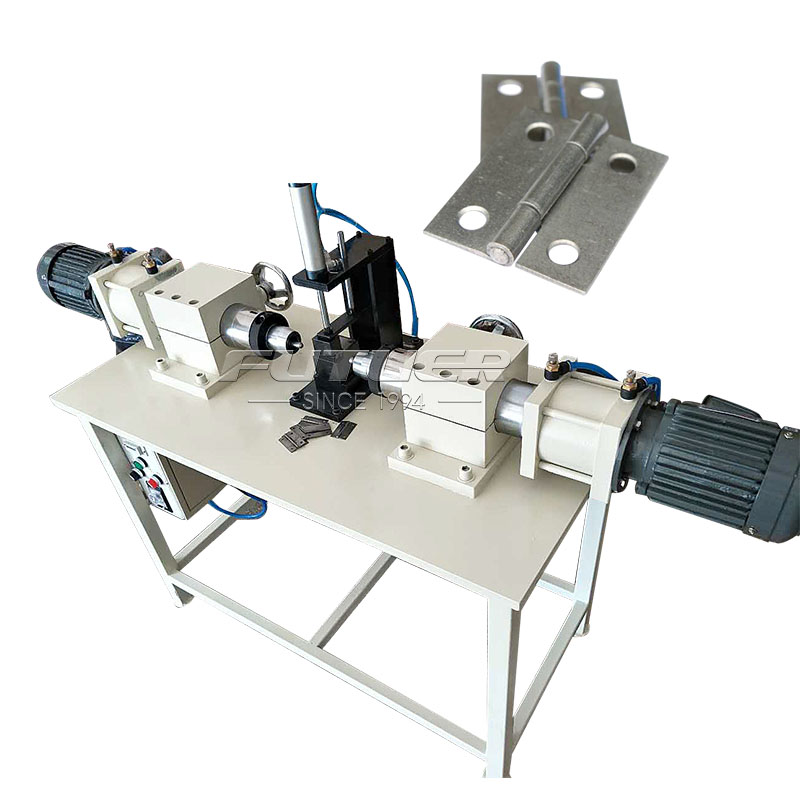
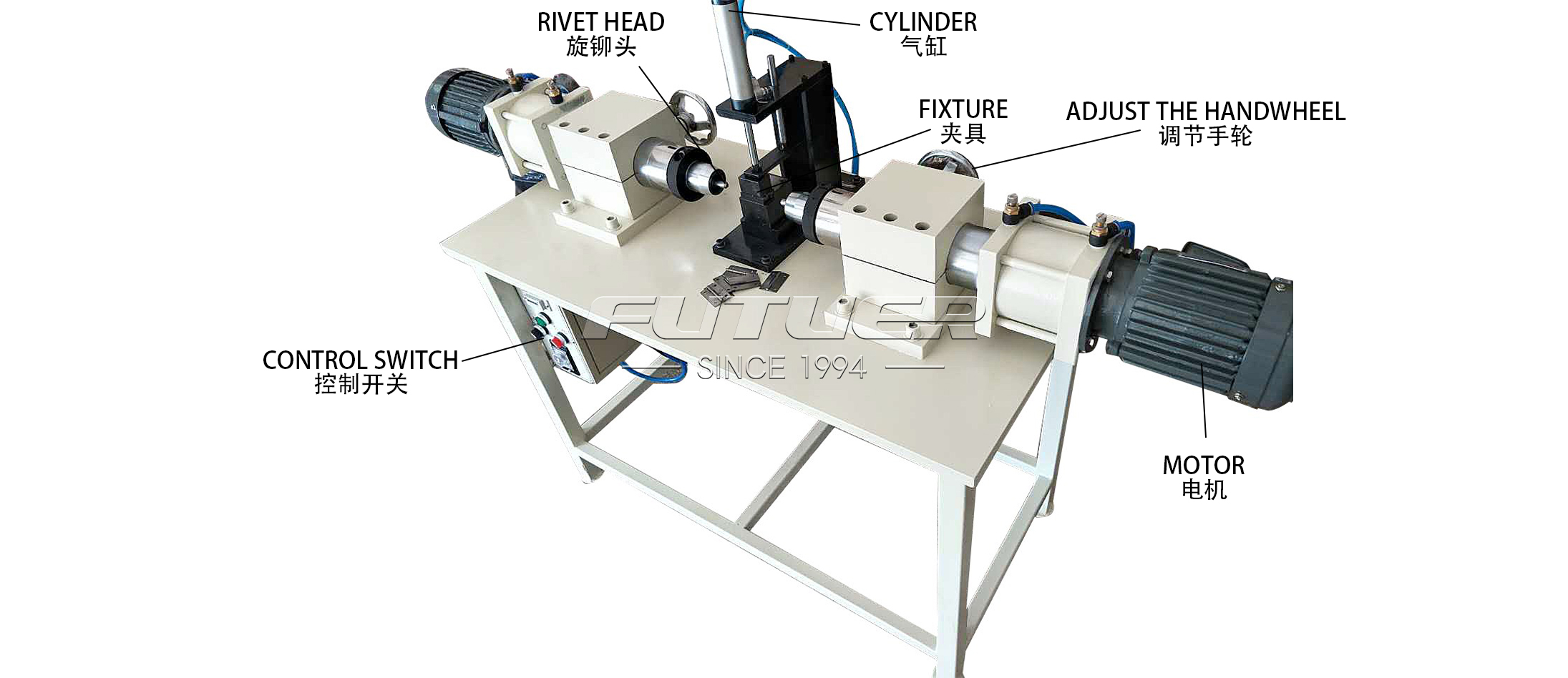
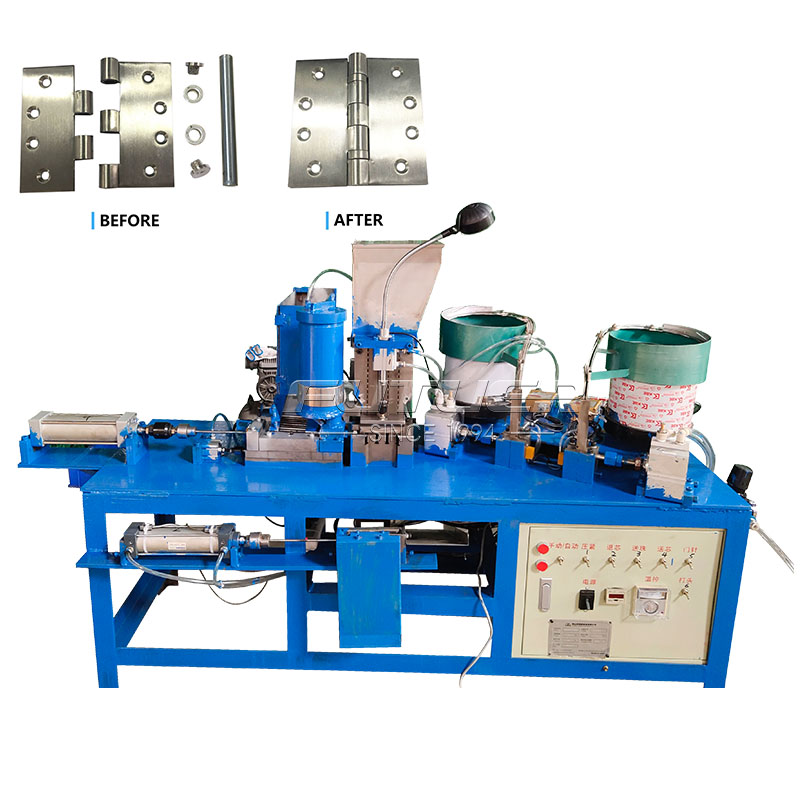
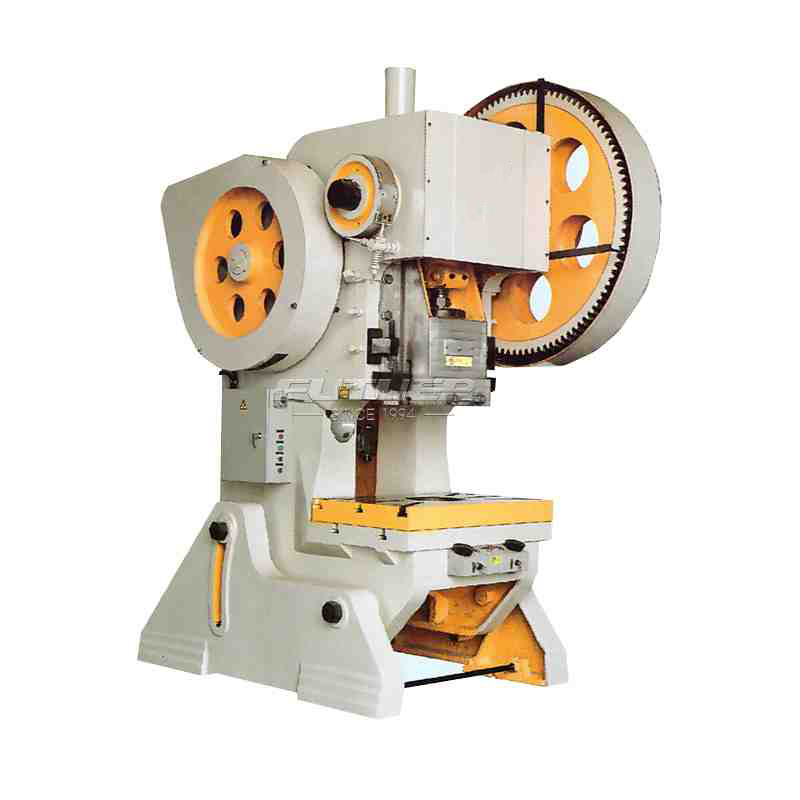
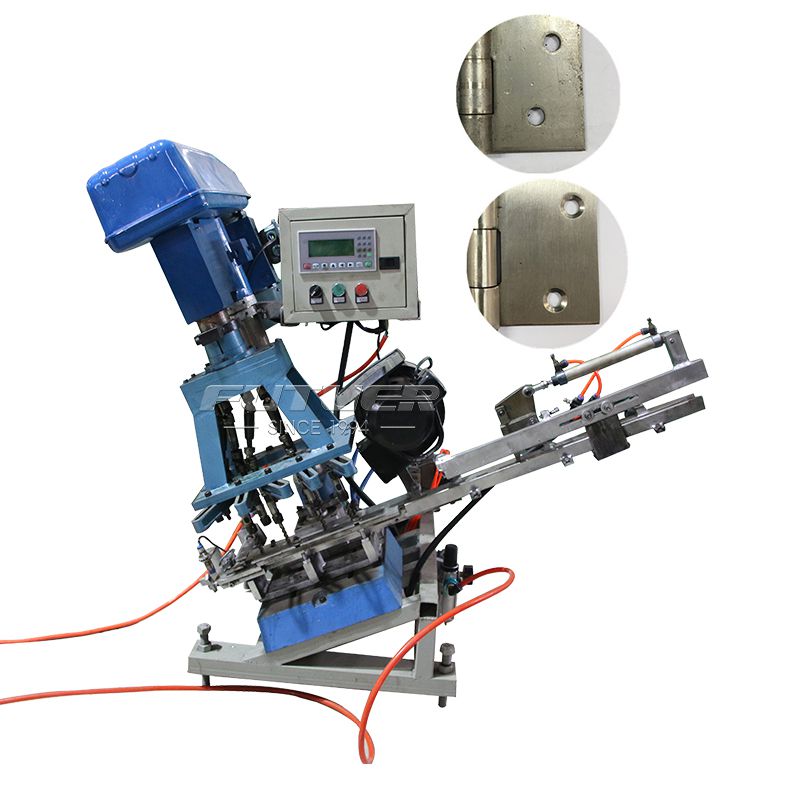
The mechanical marvel known as the hinge riveting machine has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, streamlining the process of joining hinges to various materials with unparalleled efficiency and precision.
Historical Background
The concept of riveting dates back centuries, with early civilizations using rudimentary tools to fasten materials together. However, it wasn't until the Industrial Revolution that riveting machines began to emerge, initially powered by steam and later by electricity. Over time, advancements in technology and engineering have led to the development of highly sophisticated hinge riveting machines capable of handling diverse materials and complex designs.
Components of a Hinge Riveting Machine
Frame and Base
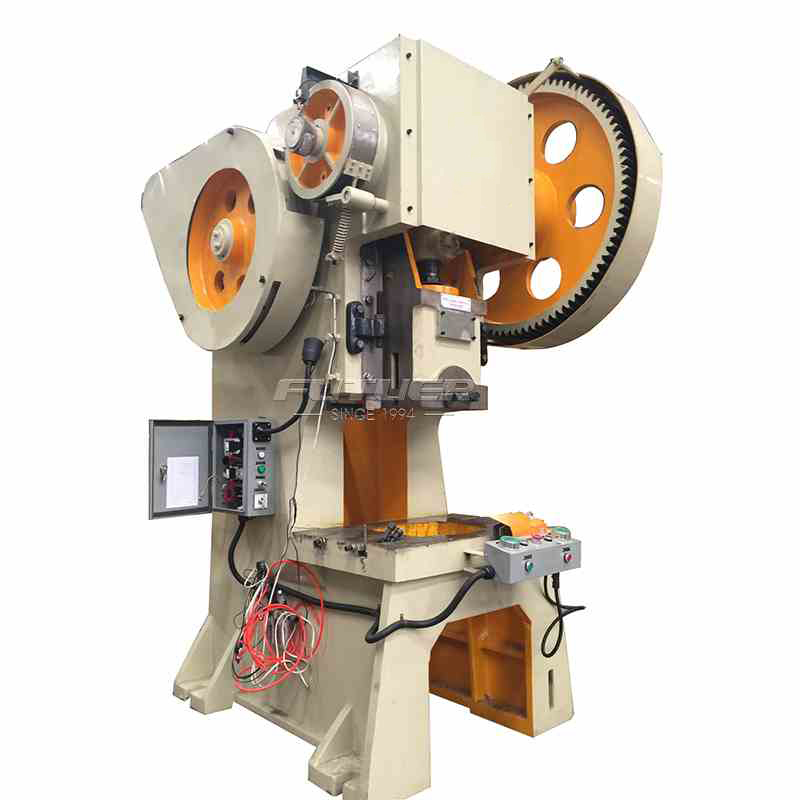
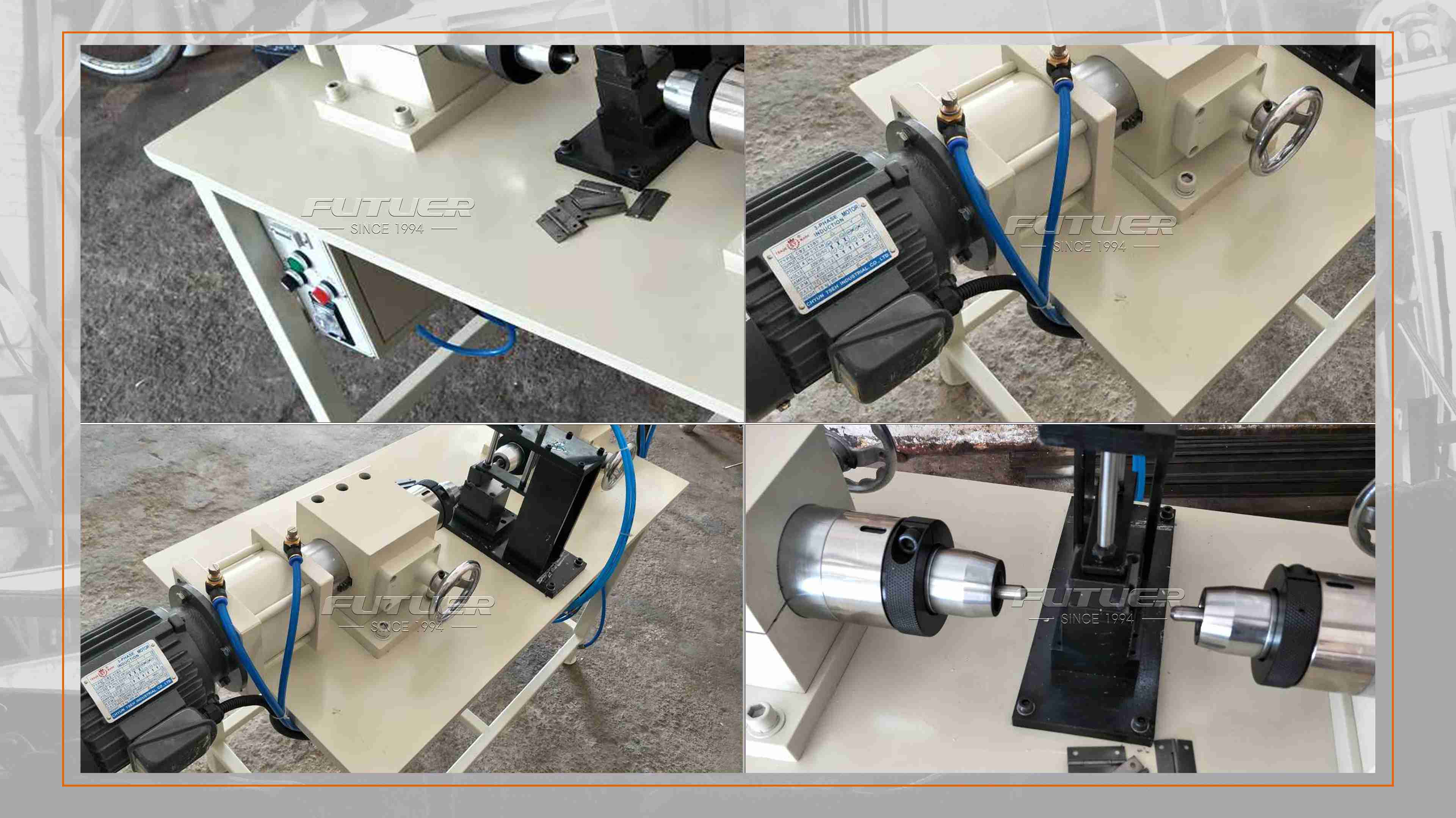
At the core of every hinge riveting machine lies a robust frame and base, providing stability and support during the riveting process. Constructed from durable materials such as steel or aluminum, the frame ensures precise alignment of components and withstands the forces generated during operation.
Riveting Mechanism
The riveting mechanism constitutes the heart of the machine and is responsible for driving and securing the rivets into the workpieces. Typically comprising a hydraulic or pneumatic system, the mechanism exerts controlled pressure to deform the rivets, creating a tight and durable joint.
Control System
Modern hinge riveting machines are equipped with advanced control systems that govern various aspects of operation, including rivet insertion force, cycle speed, and tool positioning. These systems utilize sensors and actuators to maintain optimal performance and ensure consistent results.
Safety Features
Given the potentially hazardous nature of riveting operations, hinge riveting machines are equipped with comprehensive safety features to protect operators and prevent accidents. These may include emergency stop buttons, protective guards, and interlocking mechanisms that disable the machine if safety protocols are violated.
Operating Principles
Feeding and Clamping
The riveting process begins with the feeding and clamping of the workpieces onto the machine's platform. Precision alignment is crucial to ensure accurate rivet placement and uniformity across multiple hinges.
Rivet Insertion
Once the workpieces are securely clamped, the machine automatically inserts rivets into the designated hinge locations. Depending on the design and specifications, this may involve single or multiple rivets per hinge, with precise positioning facilitated by programmable control systems.
Rivet Compression
With the rivets in place, the machine initiates the compression phase, exerting controlled force to deform the rivets and create a secure joint between the hinge and the workpiece. Hydraulic or pneumatic actuators apply consistent pressure, ensuring uniform deformation and optimal structural integrity.
Release and Ejection
Upon completion of the compression cycle, the machine releases the finished hinges, which are ready for further processing or assembly. Any excess material or debris is ejected from the machine, maintaining cleanliness and preventing contamination of the work area.
Applications and Benefits
Industrial Applications
Hinge riveting machines find widespread use across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, furniture manufacturing, and electronics. From vehicle doors and aircraft panels to cabinet doors and electronic enclosures, hinges are ubiquitous components that require precise and reliable attachment.
Advantages over Manual Riveting
Compared to traditional manual riveting methods, hinge riveting machines offer numerous advantages, including increased productivity, consistency, and worker safety. By automating the riveting process, manufacturers can significantly reduce labor costs and production times while improving overall quality and accuracy.
Precision and Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of hinge riveting machines is their ability to achieve unparalleled precision and consistency in hinge placement and rivet deformation. Programmable control systems allow for precise adjustments to accommodate various materials, hinge sizes, and design specifications, ensuring optimal performance and structural integrity.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in a hinge riveting machine may seem significant, the long-term cost savings are substantial. By eliminating the need for manual labor and minimizing material waste and rework, manufacturers can achieve higher throughput and lower production costs, ultimately enhancing profitability and competitiveness in the marketplace.
Conclusion
The hinge riveting machine represents a pinnacle of engineering innovation, offering manufacturers a reliable and efficient solution for attaching hinges to a wide range of materials. With advanced technology, robust construction, and precise control systems, these machines continue to drive productivity, quality, and safety in modern manufacturing operations.