Rubbing machines, also known as abrasion machines, play a crucial role in various industrial processes, offering precision and efficiency in surface treatment and finishing tasks. These machines are designed to apply controlled friction to workpieces, resulting in desired surface properties. Over time, rubbing machines have evolved significantly, adapting to diverse industrial needs and technological advancements.
Types of Rubbing Machines
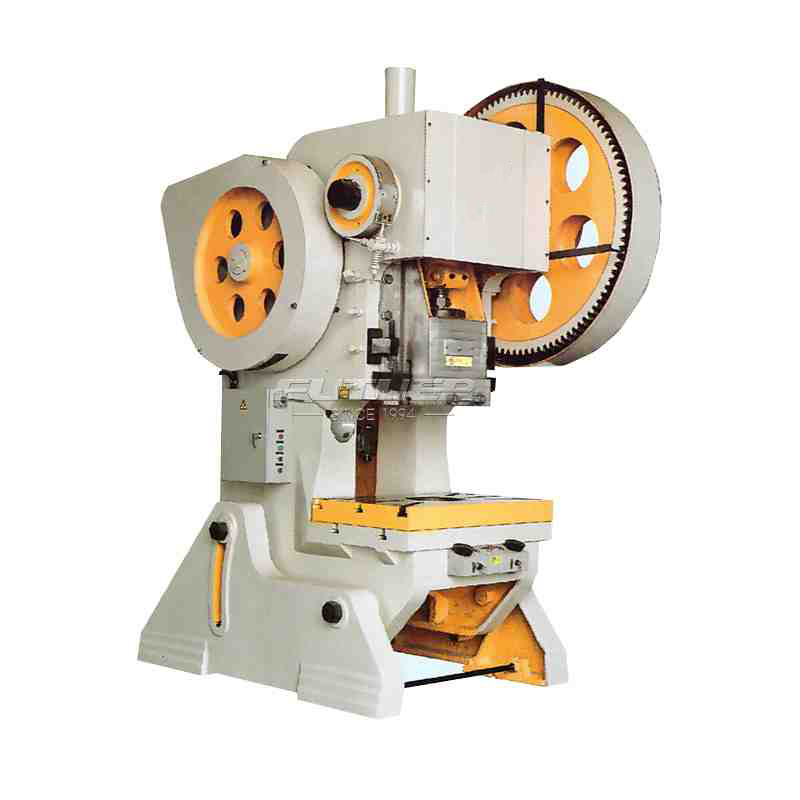
Rotary Rubbing Machines
Rotary rubbing machines feature a rotating rubbing surface that applies friction uniformly across the workpiece. This type of machine is commonly used for tasks requiring consistent surface treatment, such as polishing, buffing, and smoothing. Industries ranging from automotive to aerospace utilize rotary rubbing machines to enhance surface aesthetics and functionality.
Linear Rubbing Machines
In contrast, linear rubbing machines operate with a reciprocating motion along a linear path. These machines offer precise control over the rubbing action, making them suitable for applications demanding intricate surface detailing and dimensional accuracy. While linear rubbing machines excel in certain precision tasks, they may have limitations in handling larger workpieces or achieving high-speed operations.
Key Components of Rubbing Machines
Rubbing Surfaces
The rubbing surfaces of rubbing machines are meticulously crafted to meet specific application requirements. Various materials, including metals, ceramics, and synthetic compounds, are utilized to create durable and wear-resistant rubbing surfaces. Additionally, specialized coatings and surface treatments are applied to enhance frictional properties and prolong the lifespan of rubbing components.
Drive Systems
Efficient drive systems are integral to the operation of rubbing machines, providing the necessary power and control for precise rubbing action. Electric motors, equipped with speed controllers and torque limiters, drive the rubbing mechanisms with precision. Advanced control mechanisms, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and servo systems, enable automation and real-time adjustments, optimizing the rubbing process for consistent results.
Applications and Benefits of Rubbing Machines
Surface Treatment and Finishing
Rubbing machines are indispensable tools for achieving superior surface finishes across a wide range of materials. From metal components to plastic parts, these machines excel in polishing, deburring, and surface conditioning tasks. By removing imperfections and irregularities, rubbing machines enhance the visual appeal and functional performance of finished products, ensuring compliance with quality standards and customer expectations.
Material Removal and Precision Machining
In addition to surface treatment, rubbing machines are utilized for material removal and precision machining applications. Grinding wheels, abrasive belts, and diamond tools enable efficient stock removal and dimensional accuracy in machining operations. Whether shaping intricate components or refining critical tolerances, rubbing machines offer versatility and reliability in achieving precise outcomes.
Conclusion
Rubbing machines stand as indispensable assets in modern manufacturing and fabrication environments, offering unparalleled precision and efficiency in surface treatment and machining tasks. With continuous advancements in technology and materials, these machines continue to redefine the standards of quality and productivity across diverse industries. As the demand for precision-engineered components grows, rubbing machines will remain essential tools for achieving excellence in surface finishing and material processing.